Radiation Science
Artificial Radiation
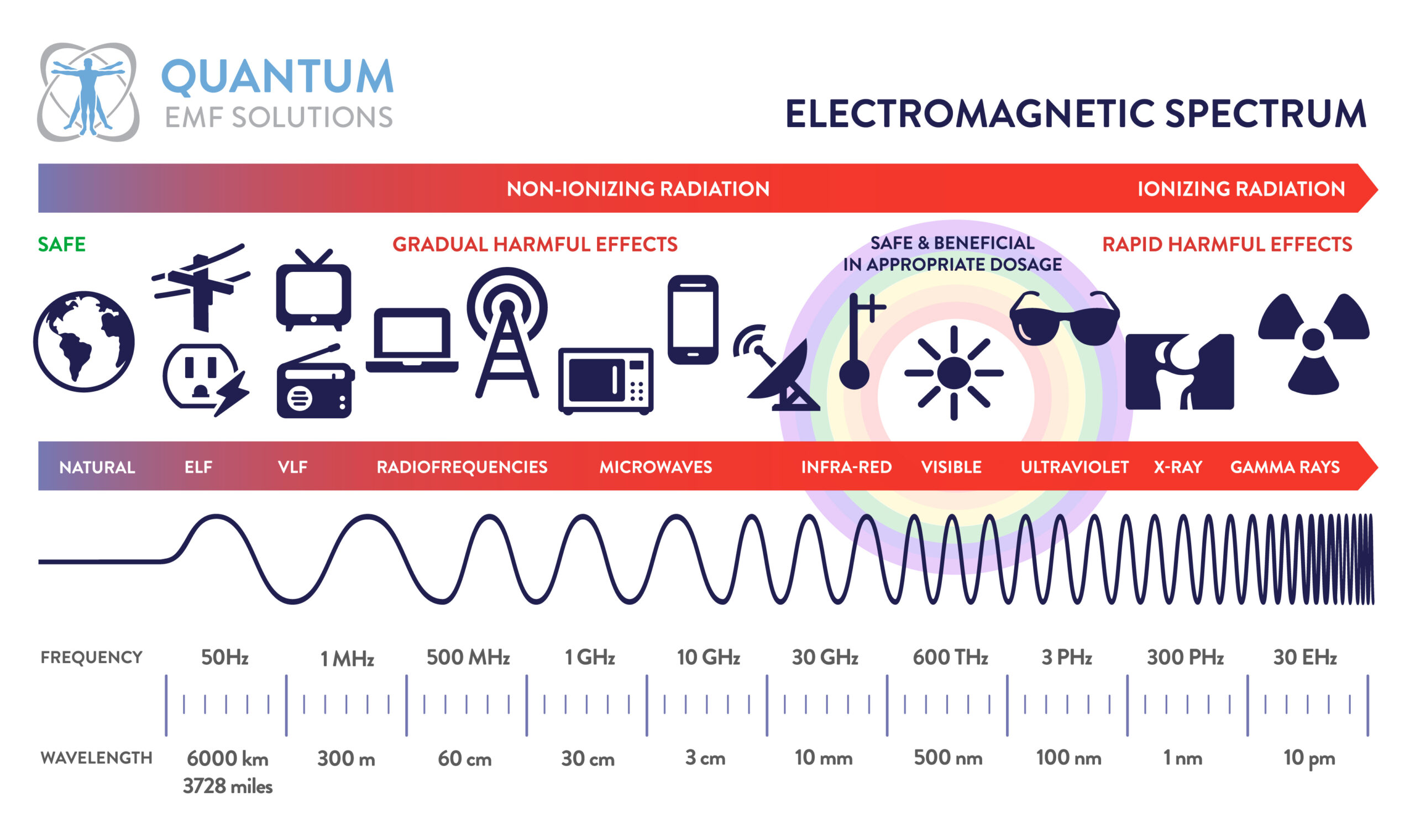
Ionizing vs Non-Ionizing
Artificial radiation can be classified into two groups: ionizing and non-ionizing radiation.
The main difference between non-ionizing and ionizing radiation lies in their ability to cause changes in atoms and molecules. The harmful effects of ionizing radiation on health are contrasted and lead to pathologies. Non-ionizing radiation is one of the most insidious forms of radiation that proceed gradually and subtly but with harmful effects. This type of radiation resides mostly within our home or office walls.

Electric Fields
Electric fields are physical phenomena created by electric charges (voltage). The strength and direction of an E-Field at any point in space can be determined by the magnitude and distribution of the charges creating the field. Alternating electric fields are essential for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. The larger the load on the conductor, the more spread the field. The frequency of electrical power in North America is 60 Hz; in other parts of the world, the standard can be 50 Hz. Most people think electricity travels within the electrical cabling and is wholly contained within these metal conductors. However, an electrical conductor functions merely as a guide. Most homes have electrical cabling emitting electric fields that can easily extend 6 feet from their source, causing bodily disturbances.
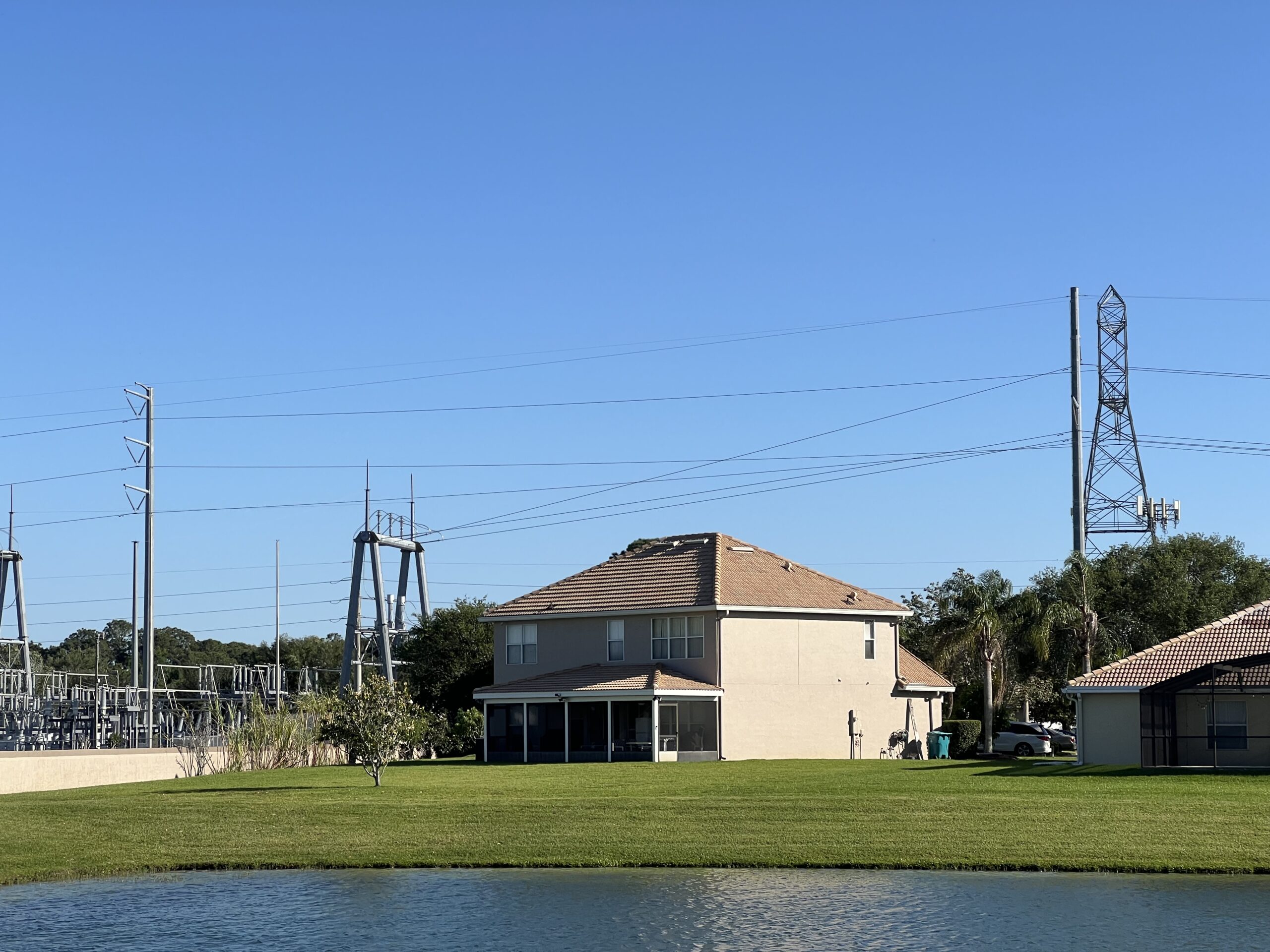
Magnetic Fields
Discovered by H.C Oersted, in 1820. Magnetic fields are physical phenomena that arise from the flow of electricity of a current-carrying wire, motors, relays, transformers, or improper wiring installations inside the home. The magnitude of these fields depends on the distance to the emission source.
They can interact with charged particles and other electromagnetic fields, such as the human body’s field, through the induction effect. They can generate parasitic body currents that can cause disturbances in the fundamental biological processes of the human body. It can cause a domino effect on the body. Epidemiological studies consistently link potential EMF exposure to increased risk of childhood leukemia and much more.


Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that propagates through space in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Its main use is to transmit information. These frequencies range from 100 KHz to 300 GHz and can be emitted by radio stations, mobile phones, cellphone towers, WIFI networks, smart TVs, or even microwave ovens FKA “Radarange Ovens.”
Studies have shown that long-term exposure to this frequency band can cause many adverse effects, i.e., oxidative stress. O.S. affects all the cells in the body and causes multi-systemic effects, targeting more than one single bodily system. Pulsed modulation used in most digital technologies can interact with fundamental biological processes of the human body. In 2011, The World Health Organization (WHO) classified the fields generated by high-frequency waves as possible carcinogens for human beings (group 2B).
